High Oleic Soybean Oil
An Excellent Choice For Health and Functionality
High oleic soybean oil boasts many benefits when compared to conventional oils and brings many attractive traits to the table. Heart-healthy with an improved fat profile, high oleic soybean oil is sustainably grown by American farmers. Additionally, the new product has a longer shelf life and an extended fry life.
HEART HEALTHY
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has recognized high oleic oils for their beneficial support of cardiovascular health.¹ High oleic soybean oil contains more than 70 percent oleic acid.²
The FDA’s high oleic oil health claim states: Supportive but not conclusive scientific evidence suggests that daily consumption of about 1.5 tablespoons (20 grams) of oils containing high levels of oleic acid, may reduce the risk of coronary heart disease. To achieve this possible benefit, oleic acid-containing oils should replace fats and oils higher in saturated fat and not increase the total number of calories you eat in a day.
Read the full qualified health claim here and view an analysis of a variety of fatty acid profiles here.
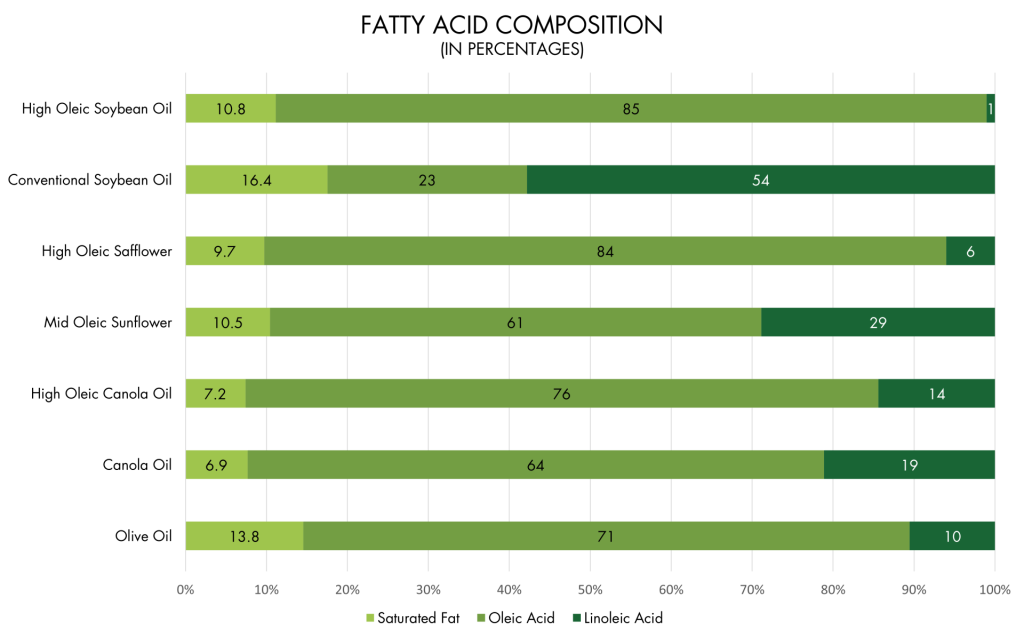
FAT PROFILE
With no trans-fat, high oleic soybean oil has an improved fat profile when compared to conventional oils and has a fatty acid composition similar to olive oil, the oil that consumers view as most healthy.³
High oleic soybean oil contains anywhere from 8.8-10.8 percent saturated fatty acid.4,5 Comparatively, olive oil contains 13.7 percent,6 canola oil contains 7 percent,7 high oleic canola oil contains 6 percent,8 and corn oil contains 13 percent.9
High oleic soybean oil contains more than 70 percent oleic acid, a healthy monounsaturated fatty acid — making it comparable to high oleic canola oil and olive oil. Canola oil contains roughly 73 percent8 and corn oil contains around 27 percent.9
High oleic soybean oil contains 3 percent of the omega-3 fatty acid alpha-linolenic acid.2Here are some additional resources that shed more light on high oleic soybean oil and fatty acid profiles in general:
- USDA study — Consumption of High-Oleic Soybean Oil Improves Lipid and Lipoprotein Profile in Humans Compared to a Palm Oil Blend: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- High oleic soybean oil fatty acid profile and effect on cardiovascular disease risk facts: Advances in Nutrition
- An overview of high oleic soybean oil: Qualisoy
- An analysis of high oleic soybean oil’s nutritional traits: Soy Connection
LONGER LASTING
When it comes to functionality, high oleic soybean oil has a longer shelf life and an extended fry life. It provides improved resistance to oxidation and reduced build-up of polymers on foodservice equipment in high-heat applications which results in less equipment maintenance and lower operating costs. High oleic soybean oil blends are also available for a customized functional solution tailored to product needs. It performs longer than standard vegetable oils in high-temperature and extended-use applications because of the heat and oxidative stability of the oil. The oxidative stability index of high oleic soybean oil is greater than 25 hours, which translates to cost savings for foodservice operations.
High oleic soybean oil is priced competitively with other high-stability alternatives. While there is a premium on high oleic soybean oil (similar to high oleic canola oil) costs will continue to decline as volume increases. Transportation costs for high oleic soybean oil are more favorable than imported alternatives and will continue to decrease as domestic availability increases.
Learn more about high oleic soybean oil’s improved functionality here and superior high oleic soybean oil value here.
AMERICAN GROWN
High oleic soybean oil is grown in the United States of America. Its use and consumption support American farmers, businesses, and the agriculture industry in general. U.S. high oleic soybean oil is sustainably grown by farm families across the country.
Learn about the sustainable practices of U.S. soybean farmers from Soy Connection here and Qualisoy here. Stay up-to-date on the latest news from the United Soybean Board here.
REFERENCES
- FDA. “FDA Completes Review of Qualified Health Claim Petition for Oleic Acid and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease.” https://www.fda.gov/food/cfsan-constituent-updates/fda-completes-review-qualified-health-claim-petition-oleic-acid-and-risk-coronary-heart-disease.
- Huth PJ, Fulgoni VL, 3rd, Larson BT. A systematic review of high-oleic vegetable oil substitutions for other fats and oils on cardiovascular disease risk factors: implications for novel high-oleic soybean oils. Adv Nutr. 2015;6(6):674-693.
- https://foodinsight.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/IFIC.Fats-and-Oils-Survey.June-2020.pdf
- Baer, D.J., Henderson, T. and Gebauer, S.K. (2021), Consumption of High‐Oleic Soybean Oil Improves Lipid and Lipoprotein Profile in Humans Compared to a Palm Oil Blend: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Lipids. https://www.ars.usda.gov/research/publications/publication/?seqNo115=379230
- Dunford, Nurhan. (2020), Properties of High Oleic Seed Oils. Available from: http://pods.dasnr.okstate.edu/docushare/dsweb/Get/Document-12062/FAPC-236web.pdf
- USDA. “Nutrients -Oil, Olive.” https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171413/nutrients
- USDA. “Nutrients -Oil, Canola.” https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172336/nutrients
- USDA. “Nutrients -Oil, High Oleic Canola.” https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171042/nutrients
- USDA. “Nutrients -Oil, Corn.” https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171029/nutrients
